Challenges and solutions in battery storage recycling
BESS are key technologies for the transition to renewable energy sources, as they allow for the storage of excess energy produced from renewable sources, such as the sun and wind, for later use. However, with the increasing deployment of these systems, the need for their sustainable recycling at the end of their life cycle also increases.
Challenges in Recycling BESS
- High Heterogeneity and Complexity: BESS often utilize various types of batteries, including lithium-ion, lead-acid, and others. Each type requires a specific recycling process, which increases the complexity and cost of recycling.
- Safety Risks Lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in BESS, can be prone to thermal runaway and fires, posing a significant safety risk during recycling.
- Logistical Challenges: Large and heavy batteries from BESS present logistical challenges in terms of their safe handling and transport to recycling centers.
- Limited Infrastructure: Despite the increased demand for battery recycling, the recycling infrastructure is often inadequate, which can lead to delays and higher costs.
Solutions and Innovations
- Advanced Recycling Technologies: The development of new technologies such as hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical methods can improve the efficiency of recycling and increase the profitability of recovering valuable materials from used batteries.
- Design for Recycling: Developing batteries with future recycling in mind can facilitate disassembly and separation of materials, thereby reducing costs and increasing the efficiency of recycling.
- Regulatory Initiatives and Policies: The establishment of strong regulatory frameworks and incentives, including extended producer responsibility (EPR), can encourage investment in recycling infrastructure and technologies.
- International Cooperation: Collaboration between countries, manufacturers, and recycling companies on sharing best practices and technologies can accelerate progress in BESS recycling.

Pie Chart – represents the distribution of materials obtained from BESS recycling, including cobalt, lithium, nickel, other metals, and non-metallic materials. This chart provides an overview of the relative importance of each material recovered from recycled batteries.
Development of Recycling Hubs
Creating regional recycling centers, known as "hubs," which specialize in various types of batteries used in BESS, could make the whole process more efficient. These hubs would enable better logistics and specialized recycling for specific materials, leading to higher efficiency and cost reduction.
Research and Development of New Materials
Investing in the research and development of new materials that are easier to recycle while maintaining or even surpassing the performance of current batteries is crucial. An example can be the development of solid-state lithium-ion batteries, which offer not only higher safety but also better recycling possibilities.
Improvement of Collection and Sorting
More efficient collection and sorting of used batteries can significantly increase the amount of material available for recycling. Digitalizing the collection process, using smart bins and sensors to monitor the status and fullness of collection points, can help increase the collection rate and the quality of sorted materials.
Collaboration with Manufacturers
Engaging battery and BESS manufacturers throughout the entire product lifecycle, from design to recycling, is essential. Initiatives such as extended producer responsibility (EPR) not only support the development of more recyclable products but also ensure the financial and logistical resources needed for effective collection and recycling.
Government Support
Government policies and financial incentives play a key role in supporting the recycling of BESS batteries. Governments can contribute through research and development grants, tax reductions for recycling companies, or the introduction of stricter regulations regarding battery recycling and disposal.
Initiatives Aimed at Increasing Recycling Efficiency
- Creation of Standardized Protocols for Recycling: The unification of recycling procedures and techniques at an international level could facilitate the exchange of best practices and make recycling processes more efficient.
- Development of Markets for Recycled Materials: Increasing demand for recycled materials from batteries could support the development of markets and the economic viability of recycling. This could include creating new applications and products that effectively utilize recycled materials.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between governments, battery manufacturers, and recycling companies can accelerate the development and implementation of innovative recycling solutions and infrastructure.
Recycling of battery energy storage systems represents a key challenge on the path to a sustainable future. While there are significant barriers, the development of new technologies, policy measures, and international cooperation pave the way for more efficient and economically viable solutions. These steps are necessary not only to minimize environmental impact but also to ensure the sustainability of energy systems.
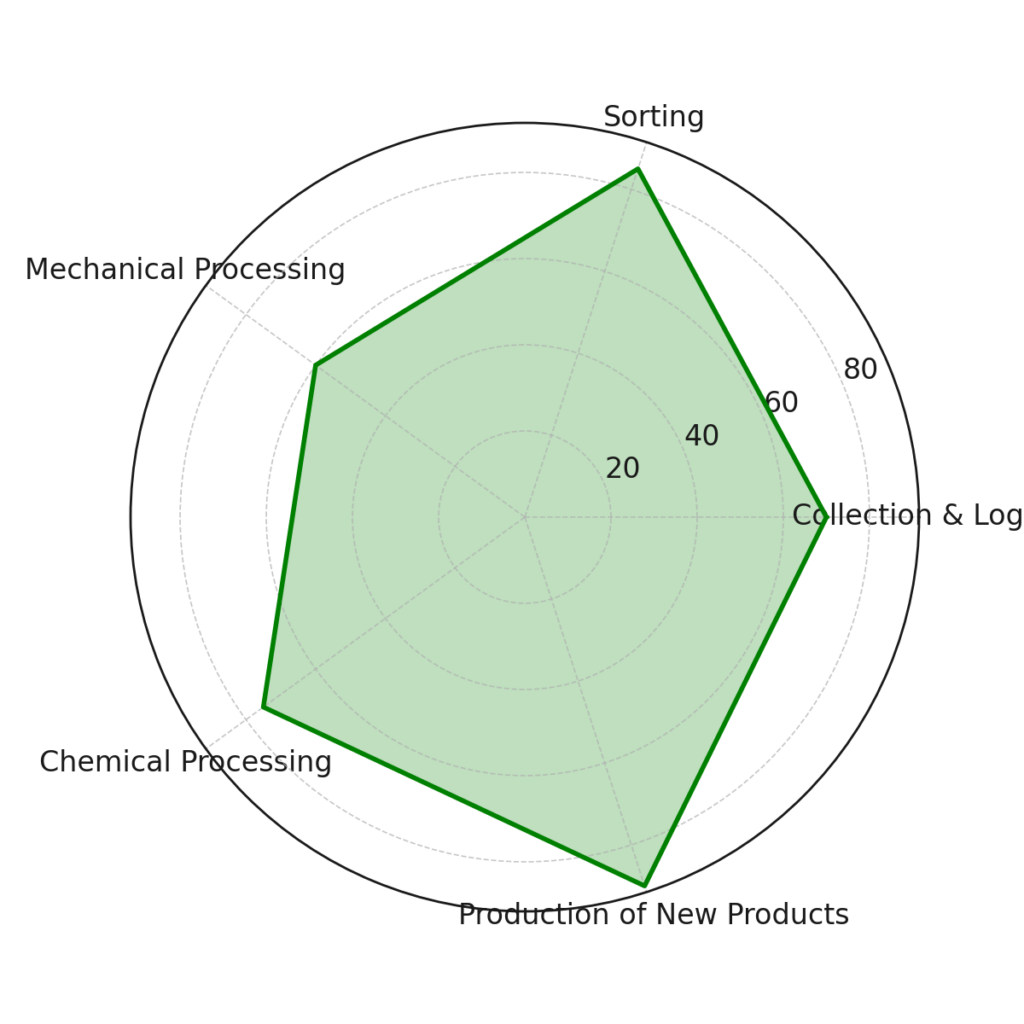
Radar Chart – displays the percentage efficiency of individual steps in the recycling process, such as collection and logistics, sorting, mechanical processing, chemical processing, and the production of new products. This chart shows which aspects of recycling are most efficient and which areas need focus for improvement.
